Shanghai and Surroundings: An Exploration of Urban Development
⏱ 2025-05-04 08:27 🔖 爱上海娱乐联盟
📢0℃
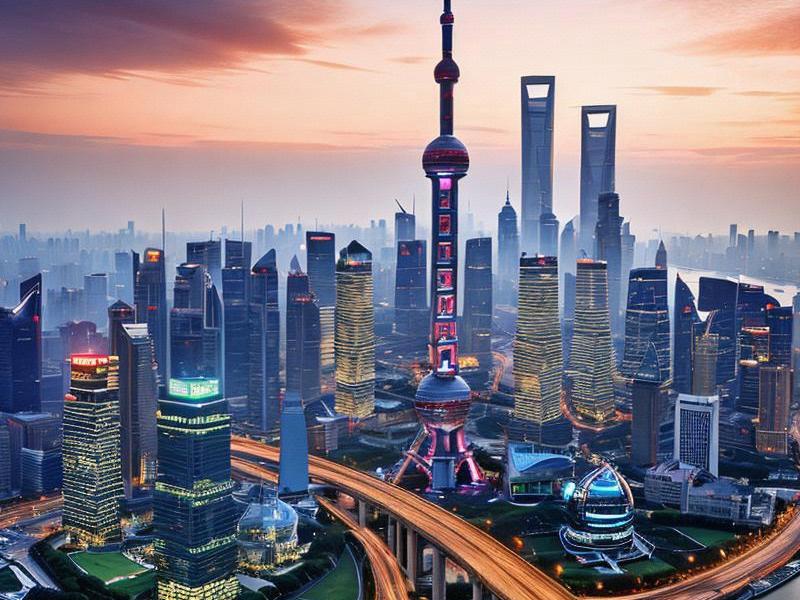

In the heart of China, where the Yangtze River meets the East China Sea, lies Shanghai, a city that has long been a beacon of economic progress and cultural exchange. Over the past few decades, Shanghai has undergone a remarkable transformation, evolving from a historic port city into a global financial hub and a model of urban development. This article explores the multifaceted aspects of Shanghai's urban development, focusing on its economic transformation, regional integration, and commitment to green development.
Economic Transformation
Shanghai's economic transformation is a story of bold reforms and strategic planning. In the late 20th century, the Chinese government designated Shanghai as one of the country's four special economic zones, alongside Shenzhen, Zhuhai, and Xiamen. This designation marked the beginning of Shanghai's rise as a global economic powerhouse.
The city's strategic location, with its deep-water port and proximity to the Yangtze River Delta, has been a key factor in its success. Shanghai's port, known as the "Gateway to China," is one of the busiest in the world, handling billions of tons of cargo annually. The city's well-developed infrastructure, including its extensive metro system, efficient public transportation, and modern airports, has further facilitated economic growth.
Shanghai's economic transformation is also evident in its financial sector. The establishment of the Shanghai Stock Exchange in 1990 marked a significant milestone in the city's journey toward becoming a global financial center. Today, Shanghai is home to numerous multinational corporations, financial institutions, and technology startups. The city's Lujiazui Financial District, often referred to as the "Wall Street of China," is a testament to its financial prowess.
Regional Integration
上海龙凤419社区 Shanghai's urban development is not confined to the city itself but extends to its surrounding areas, forming the greater Shanghai metropolitan region. This regional integration is a key strategy for sustainable urban growth and economic resilience. The Yangtze River Delta, which includes Shanghai, Jiangsu Province, and Zhejiang Province, is one of the most economically dynamic regions in China.
The integration of Shanghai with its neighboring provinces has been facilitated by various initiatives aimed at improving connectivity and fostering economic cooperation. The Shanghai-Nanjing High-Speed Railway, completed in 2010, has significantly reduced travel time between the two cities, promoting regional trade and tourism. Similarly, the Shanghai-Hangzhou High-Speed Railway, operational since 2013, has strengthened ties between Shanghai and Hangzhou, a major cultural and economic hub in Zhejiang Province.
Regional integration has also been enhanced through the development of cross-border economic zones and industrial parks. The Shanghai Free-Trade Zone, established in 2013, serves as a pilot zone for trade and investment liberalization. It has attracted numerous foreign companies and has become a model for other free-trade zones in China. Additionally, the Suzhou Industrial Park, located near Shanghai, is a joint venture between the governments of China and Singapore. It has successfully integrated advanced manufacturing, research and development, and services, creating a thriving economic ecosystem.
Green Development
As Shanghai continues to grow, it faces significant challenges related to environmental sustainability. The rapid urbanization and industrialization have led to issues such as air pollution, water scarcity, and waste management. Recognizing these challenges, the city has adopted a comprehensive approach to green development, aiming to balance economic growth with environmental protection.
One of the key strategies for green development is the promotion of renewable energy and energy efficiency. Shanghai has set ambitious targets for reducing carbon emissions and increasing the use of clean energy. The city has invested heavily in solar and wind power projects, as well as in energy-efficient buildings and public transportation systems. The expansion of the Shanghai Metro network, which now includes over 800 kilometers of track, has significantly reduced reliance on private vehicles and contributed to lower carbon emissions.
上海龙凤419会所
Shanghai has also implemented various measures to improve air quality. The city has introduced stricter emission standards for vehicles and industries, and it has promoted the use of electric vehicles through subsidies and charging infrastructure. Additionally, Shanghai has launched large-scale tree-planting programs to increase green spaces and improve air quality.
Water management is another critical aspect of Shanghai's green development efforts. The city has invested in advanced wastewater treatment facilities and has implemented measures to reduce water pollution from industrial and agricultural sources. The construction of the Qingcaosha Water Source Project, which draws water from the Yangtze River estuary, has significantly improved the city's water supply security.
Social Equity and Urban Planning
While Shanghai's urban development has brought significant economic benefits, it has also posed challenges related to social equity and urban planning. The rapid influx of people into the city has led to issues such as housing shortages, traffic congestion, and inequality. Addressing these challenges requires a holistic approach that prioritizes the well-being of all residents.
Shanghai has implemented various policies to improve housing affordability and accessibility. The city has developed large-scale public housing projects, known as "shantytown redevelopment," to provide affordable housing for low-income families. Additionally, the government has introduced measures to regulate the real estate market and prevent speculative housing purchases.
爱上海同城对对碰交友论坛 Traffic congestion is another major issue in Shanghai, with the city's population exceeding 24 million. To address this challenge, the city has invested in public transportation infrastructure and has promoted the use of bicycles and electric scooters. The introduction of ride-hailing services and the expansion of the metro network have also helped alleviate traffic congestion.
Urban planning plays a crucial role in shaping Shanghai's future. The city has adopted a master plan that emphasizes sustainable development and livability. This plan includes initiatives to preserve historical and cultural heritage, promote green spaces, and enhance the quality of life for residents. The development of waterfront areas, such as the Bund and Pudong, has transformed these former industrial zones into vibrant urban centers, offering residents and visitors a mix of cultural, recreational, and commercial activities.
Conclusion
Shanghai's urban development is a dynamic and multifaceted process that reflects the city's commitment to economic growth, regional integration, and environmental sustainability. As Shanghai continues to evolve, it faces both opportunities and challenges in balancing its aspirations as a global metropolis with the need to address social and environmental issues.
The city's economic transformation, regional integration efforts, and commitment to green development serve as a model for other cities in China and around the world. By prioritizing sustainable urban planning and social equity, Shanghai is paving the way for a more inclusive and resilient future.
In conclusion, Shanghai's journey of urban development is not just about building skyscrapers and expanding infrastructure; it is about creating a city that is livable, sustainable, and globally connected. As the city looks to the future, its ability to adapt and innovate will be crucial in addressing the complex challenges of urbanization and ensuring a prosperous and harmonious society.
Shanghai’s Fintech Renaissance: Where Bund Architecture Hosts Blockchain Revolution【外滩18号的秘密:百年建筑里的爵士复兴】Shanghai 4450: Quantum Nightlife Nexus and the Galactic Entertainment Singularity《夜上海的华丽转身:从百乐门到外滩十八号》《夜上海的三个瞬间:从礼查饭店到复兴艺术中心》Shanghai’s Quantum Nightlife: Where Imperial Gardens Host Blockchain-Powered Revelries【钢与梦的交响:上海天际线的百年叙事】Shanghai’s Green Renaissance: Where Ancient Waterways Fuel Quantum Innovation【灶披间到智能厨房:上海弄堂里的烟火进化史】Shanghai 4550: Quantum Delta Renaissance and the Galactic Sustainability Matrix