Shanghai and Its Periphery: Life and Landscapes of One of the Greatest City Regions
⏱ 2025-05-05 14:10 🔖 上海龙凤419
📢0℃
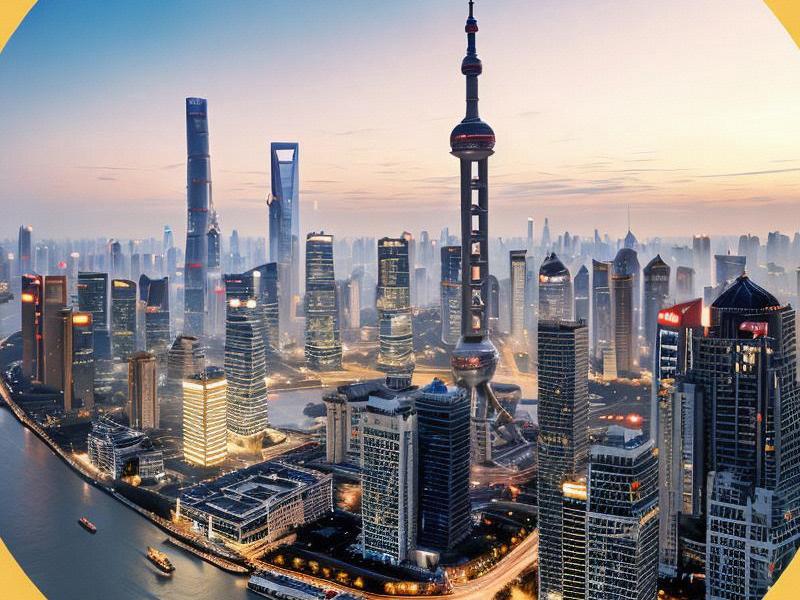

Shanghai, a global metropolis and a symbol of China's rapid economic development, is not just a city but a vast and complex city-region that extends far beyond its administrative boundaries. The periphery of Shanghai, encompassing neighboring provinces and cities such as Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Anhui, forms an intricate web of urban, rural, and industrial landscapes. This article aims to explore the life and landscapes of this remarkable city-region, shedding light on its economic vitality, cultural diversity, and the challenges and opportunities it faces.
The Economic Powerhouse of Shanghai and Its Periphery
Shanghai, as the financial and economic hub of China, plays a pivotal role in driving the national economy. Its periphery, often referred to as the "Greater Shanghai" or "Yangtze River Delta" region, is equally significant, contributing substantially to the overall economic output of the country. This region is home to some of the most advanced manufacturing facilities, high-tech industries, and financial institutions in China.
The integration of Shanghai with its periphery has been a key driver of regional economic growth. The development of transportation infrastructure, such as high-speed rail networks, highways, and seaports, has facilitated seamless connectivity between Shanghai and its neighboring areas. This has enabled the efficient movement of goods, services, and people, fostering a highly integrated regional economy.
The Yangtze River Delta region, in particular, has emerged as a global manufacturing powerhouse. It is known for its production of electronics, automobiles, machinery, and textiles, among other goods. The region's strategic location along the Yangtze River, one of the longest rivers in the world, provides access to vast markets and resources, further enhancing its economic competitiveness.
Cultural Diversity and Urbanization
上海贵人论坛
Beyond its economic prowess, Shanghai and its periphery are characterized by a rich tapestry of cultures and traditions. Shanghai itself is a melting pot of Chinese and Western influences, with its iconic skyline, historic architecture, and vibrant cultural scene. The city's cosmopolitan nature is reflected in its diverse population, which includes people from all over China and the world.
The periphery of Shanghai, on the other hand, showcases a more traditional Chinese way of life. Rural areas in Jiangsu and Zhejiang provinces are known for their picturesque landscapes, ancient temples, and well-preserved historical villages. These areas offer a glimpse into China's rich cultural heritage and provide a stark contrast to the urban sprawl of Shanghai.
Urbanization has been a defining feature of this region, with cities and towns expanding rapidly to accommodate the growing population. The development of satellite cities and new urban centers has helped alleviate the pressure on Shanghai's infrastructure and provided opportunities for economic growth and job creation in the periphery. These satellite cities, such as Kunshan, Suzhou, and Wuxi, have emerged as important economic hubs in their own right, attracting businesses and residents from across the region.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its many achievements, the Shanghai city-region faces several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure sustainable development. One of the key challenges is environmental degradation. The rapid industrialization and urbanization have led to air pollution, water contamination, and loss of biodiversity in the region. Efforts are being made to promote green development and sustainable practices, but more needs to be done to protect the environment and ensure a high quality of life for residents.
上海品茶工作室
Another challenge is the issue of regional disparities. While Shanghai and some of its neighboring cities have experienced rapid economic growth, other areas in the periphery still lag behind in terms of infrastructure, education, and healthcare. Bridging this gap requires coordinated efforts from both the central and local governments to promote balanced regional development and ensure that the benefits of economic growth are shared by all.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and growth. The Shanghai city-region has the potential to become a global leader in areas such as smart cities, green technology, and cultural tourism. By leveraging its strengths and addressing its weaknesses, the region can continue to thrive and contribute to China's overall development.
The Role of Innovation and Technology
Innovation and technology play a crucial role in shaping the future of Shanghai and its periphery. The city-region has been at the forefront of China's technological advancements, with a strong focus on research and development, digital transformation, and entrepreneurship. This has led to the emergence of numerous high-tech industries and startups, creating a vibrant innovation ecosystem.
Shanghai's status as a global financial center has further fueled its technological ambitions. The city is home to major financial institutions, fintech companies, and blockchain startups, which are driving the digital transformation of the financial sector. The development of smart cities, powered by artificial intelligence, big data, and the Internet of Things, is also transforming the way people live and work in the region.
爱上海419
The integration of Shanghai with its periphery has created opportunities for cross-regional collaboration and knowledge sharing. Universities, research institutions, and enterprises in the region are working together to develop innovative solutions to common challenges and drive economic growth. This collaborative approach has the potential to enhance the region's competitiveness and attract talent from around the world.
Cultural Tourism and Regional Identity
Cultural tourism is another area where Shanghai and its periphery have significant potential. The region's rich history, diverse cultures, and unique landscapes offer a wealth of attractions for tourists. From the modern skyscrapers of Shanghai to the ancient temples and villages of Jiangsu and Zhejiang, the region offers a wide range of experiences for visitors.
Promoting cultural tourism not only generates revenue but also helps preserve and promote the region's cultural heritage. Efforts are being made to develop cultural tourism routes, improve tourist facilities, and enhance the quality of cultural services. By leveraging its cultural assets, the Shanghai city-region can attract more tourists and position itself as a leading destination for cultural tourism in China.
At the same time, it is important to maintain a strong sense of regional identity. While globalization and urbanization bring new opportunities, they also pose risks to the preservation of local traditions and customs. The Shanghai city-region must strike a balance between embracing change and preserving its unique cultural identity.
Shanghai's Renaissance: A Journey Through the Modern Metropolis【梧桐树下的红妆与素手:上海知识女性的百年突围】Shanghai Beauties: A Glimpse into the Elegance and Diversity of Shanghai Women《海派佳人:上海美女的百年时尚演变史》Shanghai 4500: Quantum Delta Synergy and the Photonic Civilization MatrixShanghai Beauties: A Journey Through the Beauty of the City and Its People【夜色经济学:上海高端社交场所的百年嬗变】Shanghai 4550: Quantum Apex Aesthetics and the Galactic Femininity Nexus《潮汐之间:上海都市圈的文化褶皱》《鎏金年代:上海娱乐会所的时空折叠》