Shanghai and Its Peripheral Areas: A Comprehensive Analysis of Regional Development and Integration
⏱ 2025-05-01 00:14 🔖 爱上海娱乐联盟
📢0℃

Introduction
Shanghai, the bustling metropolis of China, has long been a symbol of economic prosperity and modernity. However, its story is not just confined to the city limits. The surrounding peripheral areas play a crucial role in shaping the overall development and integration of the region. This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of Shanghai and its peripheral areas, focusing on the factors that drive regional growth and the challenges that need to be addressed.
Economic Growth and Development
Shanghai's Economic Powerhouse
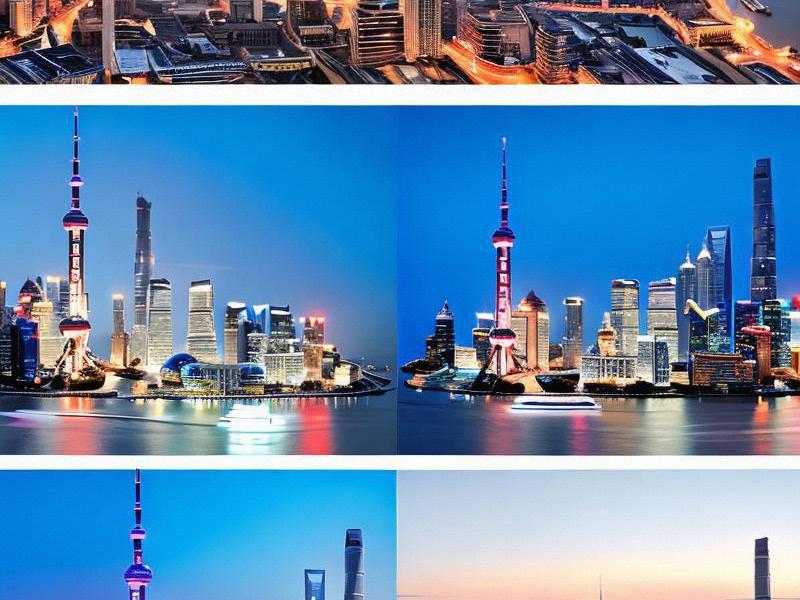
Shanghai is undoubtedly one of the most economically powerful cities in the world. With its strategic location at the mouth of the Yangtze River, it serves as a major hub for trade, finance, and logistics. The city's GDP has consistently ranked among the highest in China, driven by a robust industrial base, a thriving service sector, and a dynamic entrepreneurial ecosystem.
The financial district of Lujiazui, home to the iconic Oriental Pearl Tower and the Shanghai Tower, is a testament to Shanghai's status as a global financial center. The city's stock exchange is one of the largest in Asia, attracting investors from around the world. Additionally, Shanghai's port, the busiest container port in the world, underscores its importance in global trade.
Peripheral Areas: The Backdorpof Shanghai's Success
While Shanghai's economic prowess is well-known, the peripheral areas surrounding the city are equally significant. These regions, including Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Anhui provinces, form a critical part of the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) economic zone, which is one of the most developed and integrated regions in China.
The peripheral areas contribute significantly to Shanghai's economic growth by providing a vast pool of labor, raw materials, and markets. They also serve as important manufacturing hubs, producing goods that are either consumed locally or exported through Shanghai's ports. For instance, Suzhou and Wuxi, located in Jiangsu province, are renowned for their high-tech industries and advanced manufacturing capabilities.
Regional Integration and Synergy
夜上海最新论坛 The integration of Shanghai with its peripheral areas has been a key driver of regional development. The YRD economic zone has witnessed significant progress in infrastructure connectivity, policy coordination, and industrial collaboration. The construction of high-speed rail networks, highways, and waterways has facilitated seamless movement of people and goods across the region.
The implementation of the Yangtze River Economic Belt strategy has further enhanced regional integration. This initiative aims to promote coordinated development along the Yangtze River, leveraging its vast resources and strategic location. By fostering collaboration between Shanghai and its peripheral areas, the strategy seeks to crteeaa more integrated and competitive regional economy.
Social and Cultural Dimensions
Diverse Population and Migration
Shanghai's population is a melting pot of diverse cultures and ethnicities, reflecting its status as an international city. However, the influx of migrants from peripheral areas has played a pivotal role in shaping the city's demographic landscape. These migrants bring with them their unique traditions, skills, and perspectives, contributing to the city's cultural vibrancy.
The peripheral areas, in turn, are influenced by the urban culture and lifestyle of Shanghai. The migration of people and ideas between the city and its surrounding regions fosters a sense of interconnectedness and shared identity. This cultural exchange enriches both Shanghai and its peripheral areas, creating a more cohesive and harmonious regional community.
Education and Innovation
Education and innovation are key drivers of regional development, and both Shanghai and its peripheral areas have made significant strides in these areas. Shanghai is home to world-class universities and research institutions, such as Fudan University and Tongji University, which attract top talent from across the country and abroad. These institutions play a crucial role in advancing scientific research, fostering innovation, and nurturing the next generation of leaders.
The peripheral areas have also invested heavily in education and innovation, recognizing their importance in driving economic growth. Cities like Nanjing and Hangzhou, located in Jiangsu and Zhejiang provinces respectively, have emerged as hubs for technology and entrepreneurship. These cities boast a strong presence of high-tech industries, startups, and research institutions, contributing to the overall innovation ecosystem of the region.
Infrastructure and Urbanization
上海贵族宝贝自荐419
Modern Infrastructure
Shanghai's modern infrastructure is a cornerstone of its economic success. The city boasts a comprehensive transportation network, including an extensive metro system, international airports, and efficient roadways. These facilities facilitate the movement of people and goods, supporting the city's dynamic economy.
The peripheral areas have also made significant investments in infrastructure, enhancing their connectivity with Shanghai. The construction of high-speed rail lines, such as the Shanghai-Nanjing and Shanghai-Hangzhou lines, has reduced travel times and increased accessibility. Additionally, the development of smart cities and digital infrastructure is transforming the way people live and work in the region.
Urbanization and Spatial Planning
Urbanization is a defining feature of Shanghai and its peripheral areas. The rapid expansion of urban areas has brought about significant changes in land use, housing, and public services. Effective spatial planning is essential to ensure sustainable urban development and address the challenges of congestion, pollution, and inequality.
Shanghai has implemented various measures to manage urbanization, such as promoting mixed-use developments, enhancing green spaces, and improving public transportation. The city's master plan emphasizes the importance of creating livable and sustainable urban environments, balancing economic growth with social and environmental considerations.
Challenges and Opportunities
Environmental Sustainability
One of the major challenges facing Shanghai and its peripheral areas is environmental sustainability. The rapid industrialization and urbanization have led to issues such as air pollution, water contamination, and deforestation. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders, including government agencies, businesses, and citizens.
上海花千坊龙凤 The adoption of green technologies and sustainable practices is crucial in mitigating environmental impacts. Shanghai has been a pioneer in promoting renewable energy, energy-efficient buildings, and waste management initiatives. The peripheral areas can learn from these experiences and adopt similar strategies to achieve sustainable development.
Regional Disparities
Another challenge is the existence of regional disparities in terms of economic development, infrastructure, and public services. While Shanghai enjoys a high standard of living, some peripheral areas still face poverty and underdevelopment. Bridging these gaps requires targeted policies and investments to promote balanced regional growth.
The government has launched various initiatives to address regional disparities, such as the Western Development Strategy and the revitalization of old industrial bases. These efforts aim to stimulate economic activity, improve infrastructure, and enhance public services in underdeveloped regions, fostering a more equitable and inclusive regional development.
Opportunities for Collaboration
Despite the challenges, there are significant opportunities for collaboration between Shanghai and its peripheral areas. The integration of the YRD economic zone presents a unique opportunity to leverage complementary strengths and achieve mutual benefits. By fostering collaboration in areas such as trade, investment, innovation, and environmental protection, the region can unlock its full potential and drive sustainable growth.
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) also offers new opportunities for regional development. By connecting Shanghai and its peripheral areas with other parts of China and the world, the BRI can enhance trade, investment, and cultural exchanges, creating a more interconnected and prosperous region.
Conclusion
Shanghai and its peripheral areas form a dynamic and integrated regional economy that plays a crucial role in China's development. The city's economic power, cultural vibrancy, and modern infrastructure are complemented by the resources, skills, and perspectives of its surrounding regions. While challenges such as environmental sustainability and regional disparities need to be addressed, the opportunities for collaboration and growth are immense.
By fostering regional integration, adopting sustainable practices, and addressing disparities, Shanghai and its peripheral areas can crteeaa more prosperous, inclusive, and sustainable future. The journey towards regional development and integration is ongoing, and the experiences of this dynamic region offer valuable lessons for other parts of the world.
Shanghai’s Fintech Renaissance: Where Bund Architecture Hosts Blockchain Revolution【外滩18号的秘密:百年建筑里的爵士复兴】Shanghai 4450: Quantum Nightlife Nexus and the Galactic Entertainment Singularity《夜上海的华丽转身:从百乐门到外滩十八号》《夜上海的三个瞬间:从礼查饭店到复兴艺术中心》Shanghai’s Quantum Nightlife: Where Imperial Gardens Host Blockchain-Powered Revelries【钢与梦的交响:上海天际线的百年叙事】Shanghai’s Green Renaissance: Where Ancient Waterways Fuel Quantum Innovation【灶披间到智能厨房:上海弄堂里的烟火进化史】Shanghai 4550: Quantum Delta Renaissance and the Galactic Sustainability Matrix